Psoriasis- Signs, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
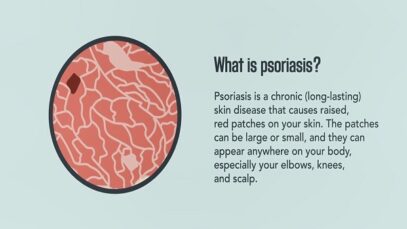
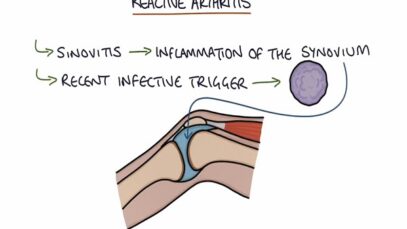
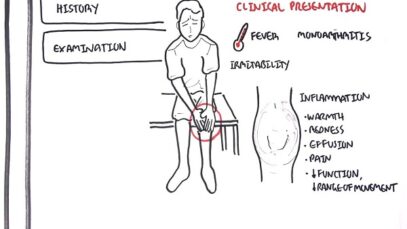
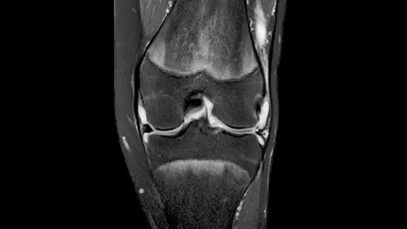
Clinical presentation •Variants The major clinical forms of psoriasis are similar in children and adults. Chronic plaque psoriasis is the most common form of psoriasis in children. Guttate, pustular, and erythrodermic psoriasis are less frequent. Chronic plaque psoriasis is characterized by the presence of well-demarcated, erythematous plaques with silvery-white, mica-like scale. In children with highly […]