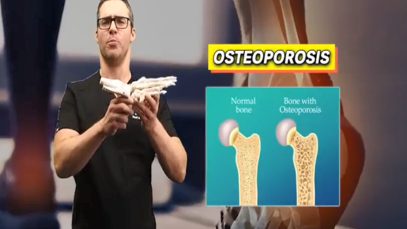
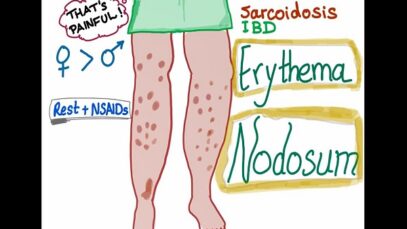
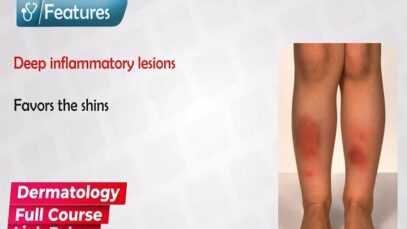
Rheumatology27 Videos



Psoriasis vulgaris – Ursachen, Symptome und Behandlung – dermanostic Hautlexikon
Pathophysiology of plaque psoriasis ●Psoriasis is a complex immune-mediated disorder that presents as inflammatory plaques in the skin. Dysregulation or alteration of components of the innate and adaptive immune systems, keratinocyte function, and vascular structure contribute to the manifestations of this disease. ●Plasmacytoid and myeloid dendritic cells are key contributors to development of inflammation in […]