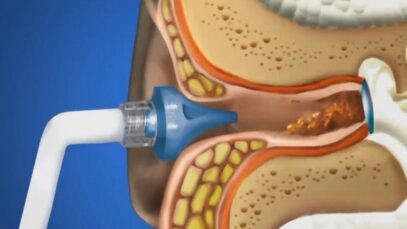
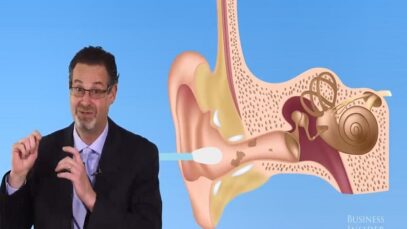
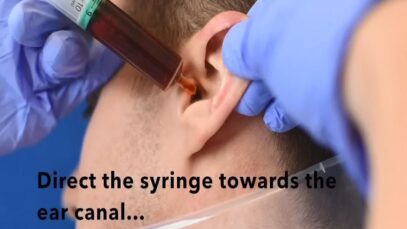
Ear Irrigation
Pathogenesis, clinical features, and diagnosis The term external otitis (also known as otitis externa or swimmer’s ear) refers to inflammation of the external auditory canal or auricle, usually from infection. ●Risk factors Risk factors for developing external otitis include swimming (or other water exposure), trauma (eg, ear scratching, cotton swabs), occlusive ear devices […]