Abdomen33 Videos



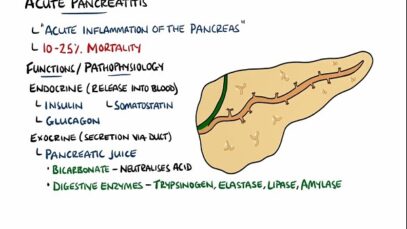
Acute Pancreatitis – Causes, Signs Symptoms, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis
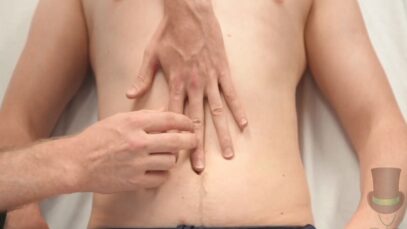
Clinical features The majority of patients with acute pancreatitis have acute onset of severe upper abdominal pain. Patients may have associated nausea and vomiting. On physical examination, patients have abdominal tenderness to palpation. Patients with severe acute pancreatitis may have fever, tachypnea, tachycardia, hypoxemia, and hypotension. Laboratory findings Early in the course of acute pancreatitis, […]
Normal Abdominal _ Pelvic CT Anatomy_ Algorithm – Radiology
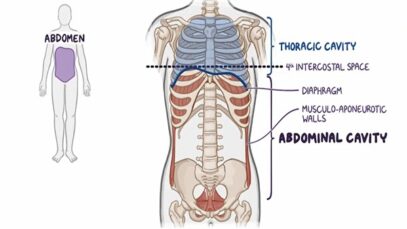
Structure and Function The abdomen consists of the organs necessary for digestion. These include the stomach, pancreas, liver, gallbladder and small and large intestines. The abdomen also contains the kidneys and spleen. Connecting tissues called the mesentery, hold these organs together. The mesentery also allows these organs to move relative to one another and expand. […]
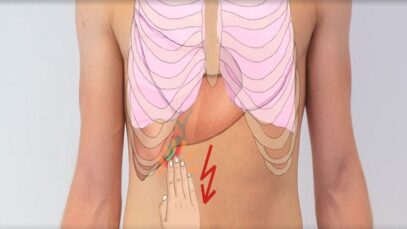
Murphy’s sign – clinical examination
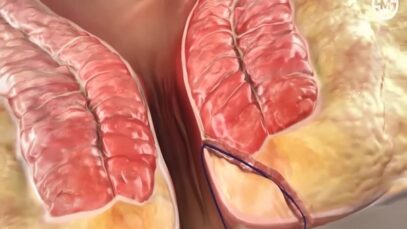
Overview of gallstone disease in adults ●Clinical presentation •Asymptomatic The majority of patients with gallstones are asymptomatic and will remain so throughout their lives. Of those with incidental (asymptomatic) gallstones, approximately 15 to 25 percent will become symptomatic after 10 to 15 years of follow-up. •Biliary colic Patients with symptomatic uncomplicated gallstone disease typically […]
Acute pancreatitis
Predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis Scoring systems During the initial 24 hours, severe acute pancreatitis (AP) can be predicted using clinical, laboratory, and radiologic risk factors, many of which have been incorporated into scoring systems such as the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) score, the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Examination (APACHE) II score, […]
Paracentesis #Ascitic tap
Evaluation of adults with ascites ●Etiology There are numerous causes of ascites, but the most common cause of ascites in the United States is cirrhosis. Other common causes of ascites include malignancy-related ascites and ascites due to heart failure. Approximately 5 percent of patients will have two or even three causes for ascites formation. […]